Pass Cisco 300-115 exam in an easy way with real exam practice questions and answers. Free Cisco 300-115 exam test practice materials and study guides online demo download.
QUESTION 1
An access switch has been configured with an EtherChannel port. After configuring SPAN to monitor this port, the network administrator notices that not all traffic is being replicated to the management server. What is a cause for this issue?
A. VLAN filters are required to ensure traffic mirrors effectively.
B. SPAN encapsulation replication must be enabled to capture EtherChannel destination traffic.
C. The port channel can be used as a SPAN source, but not a destination.
D. RSPAN must be used to capture EtherChannel bidirectional traffic.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
A source port or EtherChannel is a port or EtherChannel monitored for traffic analysis. You can configure both Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports and EtherChannels as SPAN sources. SPAN can monitor one or more source ports or EtherChannels in a single SPAN session. You can configure ports or EtherChannels in any VLAN as SPAN sources. Trunk ports or EtherChannels can be configured as sources and mixed with nontrunk sources. A port-channel interface (an EtherChannel) can be a SPAN source, but not a destination.
QUESTION 2
Refer to the exhibit.
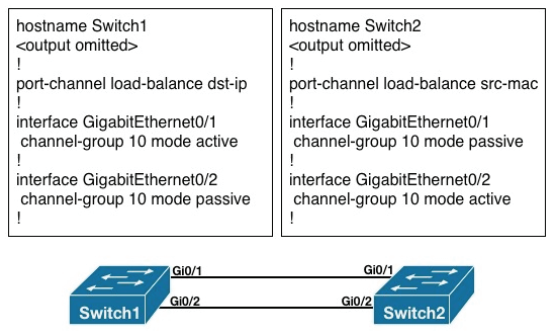
What is the result of the configuration?
A. The EtherChannels would not form because the load-balancing method must match on the devices.
B. The EtherChannels would form and function properly even though the load-balancing and EtherChannel modes do not match.
C. The EtherChannels would form, but network loops would occur because the load-balancing methods do not match.
D. The EtherChannels would form and both devices would use the dst-ip load-balancing method because Switch1 is configured with EtherChannel mode active.
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
An etherchannel will form if one end is active and the 300-115 other is passive. The table below sum- marizes the results for LACP channel establishment based on the configuration of each side of a link:
LACP Channel Establishment
S1 S2 Established?
On On Yes
Active/Passive Active Yes
On/Active/Passive Not Configured No
On Active No
Passive/On Passive No
Load balancing can only be configured globally. As a result, all channels (manually configured, PagP, or LACP) use the same load-balancing. This is true for the switch globally, although each switch involved in the etherchannel can have non matching parameters for load balancing.
QUESTION 3
A network engineer tries to configure storm control on an EtherChannel bundle. What is the result of the configuration?
A. The storm control settings will appear on the EtherChannel, but not on the associated physical ports.
B. The configuration will be rejected because storm control is not supported for EtherChannel.
C. The storm control configuration will be accepted, but will only be present on the physical interfaces.
D. The settings will be applied to the EtherChannel bundle and all associated physical interfaces.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
After you configure 300-115 an EtherChannel, any configuration that you apply to the port-channel interface affects the EtherChannel; any configuration that you apply to the physical interfaces affects only the interface where you apply the configuration. Storm Control is an exception to this rule. For example, you cannot configure Storm Control on some of the members of an EtherChannel; Storm Control must be configured on all or none of the ports. If you configure Storm Control on only some of the ports, those ports will be dropped from the EtherChannel interface (put in suspended state). Therefore, you should configure Storm Control at the EtherChannel Interface level, and not at the physical interface level.
QUESTION 4
What is the function of NSF?
A. forward traffic simultaneously using both supervisors
B. forward traffic based on Cisco Express Forwarding
C. provide automatic failover to back up supervisor in VSS mode
D. provide nonstop forwarding in the event of failure of one of the member supervisors
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
VSS is network system virtualization technology that pools multiple Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches into one virtual switch, increasing operational efficiency, boosting nonstop communications, and scaling system bandwidth capacity to 1.4 Tbps. Switches would operate as a single logical virtual switch called a virtual switching system 1440 (VSS1440). VSS formed by two Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches with the Virtual Switching Supervisor 720-10GE. In a VSS, the data plane and switch fabric with capacity of 720 Gbps of supervisor engine in each chassis are active at the same time on both chassis, combining for an active 1400-Gbps switching capacity per VSS. Only one of the virtual switch members has the active control plane. Both chassis are kept in sync with the 300-115 inter-chassis Stateful Switchover (SSO) mechanism along with Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) to provide nonstop communication even in the event of failure of one of the member supervisor engines or chassis.
Read more: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/exams/current-list/switch2.html


