QUESTION 1
Which statement is true about the PPP Session Phase of PPPoE?
http://www.leads4pass.com/300-101.html Cisco Certification Exam Material 300-101 Exam Dumps
Latest and most Accurate Cisco 300-101 exam material and real exam practice questions and answers.
A. PPP options are negotiated and authentication is not performed. Once the link setup is completed, PPPoE functions as a Layer 3 encapsulation method that allows data to be transferred over the PPP link within PPPoE headers.
B. PPP options are not negotiated and authentication is performed. Once the link setup is completed, PPPoE functions as a Layer 4 encapsulation method that allows data to be transferred over the PPP link within PPPoE headers.
C. PPP options are automatically enabled and authorization is performed. Once the link setup is completed, PPPoE functions as a Layer 2 encapsulation method that allows data to be encrypted over the PPP link within PPPoE headers.
D. PPP options are negotiated and authentication is performed. Once the link setup is completed, PPPoE functions as a Layer 2 encapsulation method that allows data to be transferred over the PPP link within PPPoE headers.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
PPPoE is composed of two main phases:
Active Discovery Phase–In this phase, the PPPoE client locates a PPPoE server, called an access concentrator. During this phase, a Session ID is assigned and the 300-101 PPPoE layer is established.
PPP Session Phase–In this phase, PPP options are negotiated and authentication is performed. Once the link setup is completed, PPPoE functions as a Layer 2 encapsulation method, allowing data to be transferred over the PPP link within PPPoE headers.
QUESTION 2
Refer to the exhibit.
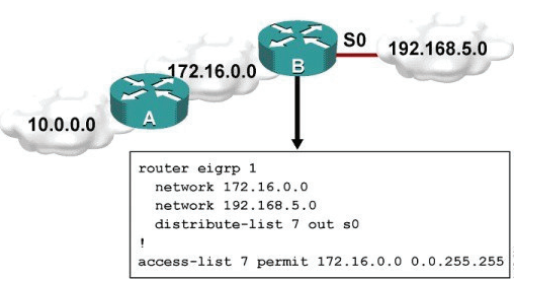
Which one statement is true?
A. Traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network will be blocked by the ACL.
B. The 10.0.0.0/8 network will not be advertised by Router B because the network statement for the 10.0.0.0/8 network is missing from Router B.
C. The 10.0.0.0/8 network will not be in the routing table on Router B.
D. Users on the 10.0.0.0/8 network can successfully ping users on the 192.168.5.0/24 network, but users on the 192.168.5.0/24 cannot successfully ping users on the 10.0.0.0/8 network.
E. Router B will not advertise the 10.0.0.0/8 network because it is blocked by the ACL.
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
You can filter what individual routes are sent (out) or received (in) to any interface within your EIGRP configuration.
One example is noted above. If you 300-101 filter outbound, the next neighbor(s) will not know about anything except the 172.16.0.0/16 route and therefore won’t send it to anyone else downstream. If you filter inbound, YOU won’t know about the route and therefore won’t send it to anyone else downstream.
QUESTION 3
A router with an interface that is configured with ipv6 address autoconfig also has a link-local address assigned. Which message is required to obtain a global unicast address when a router is present?
A. DHCPv6 request
B. router-advertisement
C. neighbor-solicitation
D. redirect
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Autoconfiguration is performed on multicast-enabled links only and begins when a multicast- enabled interface is enabled (during system startup or manually).
Nodes (both, hosts and routers) begin the process by generating a link-local address for the interface. It is formed by appending the interface identifier to wellknown link-local prefix FE80 :: 0. The interface identifier replaces the right-most zeroes of the link-local prefix. Before the link-local address can be assigned to the interface, the node performs the Duplicate Address Detection mechanism to see if any other node is using the 300-101 same link-local address on the link. It does this by sending a Neighbor Solicitation message with target address as the “tentative” address and destination address as the solicited-node multicast address corresponding to this tentative address. If a node responds with a Neighbor Advertisement message with tentative address as the target address, the address is a duplicate address and must not be used.
Hence, manual configuration is required.
Once the node verifies that its tentative address is unique on the link, it assigns that link-local address to the interface. At this stage, it has IP-connectivity to other neighbors on this link. The autoconfiguration on the routers stop at this stage, further tasks are performed only by the hosts. The routers will need manual configuration (or stateful configuration) to receive site-local or global addresses.
Read more: http://www.leads4pass.com/300-101.html The next phase involves obtaining Router Advertisements from routers if any routers are present on the link. If no routers are present, a stateful configuration is required. If routers are present, the Router Advertisements notify what sort of configurations the hosts need to do and the hosts receive a global unicast IPv6 address.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/exams/current-list/route2.html
Download free Cisco 300-101 exam pdf files: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B7LFs7RuvDV4WlBkZy10MDZUbnM
Watch the video to learn more:


