300-410 Dumps [2022] Pass 300-410 ENARSI Exam on First Attempt
You can use the 300-410 dumps to make you successful the first time you take the 300-410 ENARSI exam.
Newly updated 300-410 dumps https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html to help you successfully pass the Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) best preparation materials.
548 newly updated 300-410 dumps verified by a team of seasoned experts, including PDF and VCE learning modes so you can easily study in any environment, and pass the Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) exam in one pass.
leads4pass 300-410 dumps have real-world exam room success and guaranteed high scores to help you pass the 300-410 ENARSI Exam with ease.
300-410 Free dumps available for you to read online
QUESTION 1
Refer to the exhibit. Users report that IP addresses cannot be acquired from the DHCP server. The DHCP server is configured as shown. About 300 total nonconcurrent users are using this DHCP server, but none of them are active for more than two hours per day. Which action fixes the issue within the current resources?
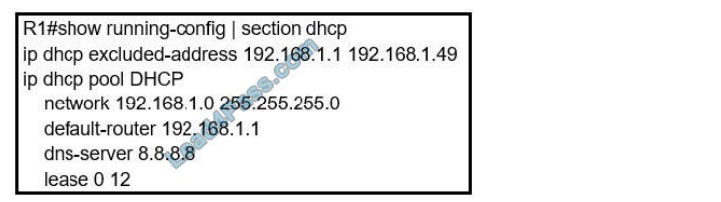
A. Modify the subnet mask to the network 192.168.1.0 255.255.254.0 command in the DHCP pool
B. Configure the DHCP lease time to a smaller value
C. Configure the DHCP lease time to a bigger value
D. Add the network 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 command to the DHCP pool
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 2
Which of the following IPv6/IPv4 interoperability techniques routes both IP versions simultaneously?
A. NAT-PT
B. Dual stack
C. 6to4 tunnels
D. Teredo
Correct Answer: B
When the routers in the network are capable of routing both IPv6 and IPv4 traffic, it is referred to as dual-stack. The dual-stack routers simply recognize the version a frame is using and react accordingly to each frame.
Network Address Translation- Port Translation (NAT-PT) is a service that runs on a router or server that converts IPv4 traffic to IPv6 and vice versa. This eliminates the need for the routers or clients to be dual stack-capable. When only one router exists between the IPv4 and the IPv6 networks, this will be the only option since all other methods listed require a dual-stack capable device on each end of the tunnel. The IPv6 to IPv4 mapping can be obtained by the host from a DNS server, or the mapping can be statically defined on the NAT device.
6to4 tunnels can be created between dual-stack routers or between a dual-stack router and a dual-stack client. In either case, each tunnel endpoint will have both an IPv6 and an IPv4 address. When traffic needs to cross an area where IPv6 is not supported, the tunnel can be used to transport the IPv6 packet within an IPv4 frame. When the frame reaches the end of the tunnel, the IPv4 header is removed and the IPv6 frame is further routed based on its IPv6 address.
Teredo is an alternate tunneling mechanism that encapsulates the IPv6 frame in an IPv4 UDP packet. It has the added benefit of traversing a NAT device that is converting private IP addresses to public IP addresses. 6to4 tunnels cannot traverse NAT devices by converting private IP addresses to public IP addresses.
Objective:
Network Principles
Sub-Objective:
Recognize proposed changes to the network
References:
Cisco > Home > Products and Services > Cisco IOS and NX-OS Software > Cisco IOS Technologies > IPV6 > Product
Literature > White Papers > Federal Agencies and the Transition to IPv6 Cisco > Cisco IOS IPv6 Configuration Guide,
Release 15.2MT
QUESTION 3
Which conditions will prevent two EIGRP routers from becoming neighbors? (Choose two.)
A. Their K-values do not match.
B. Their hold times do not match.
C. Their AS numbers do not match.
D. Their hello intervals do not match.
Correct Answer: AC
EIGRP routers will not become neighbors if the K-values do not match or if the autonomous system (AS) numbers do not match. They also will not become neighbors if EIGRP is not enabled for the proper networks on the local and remote routers. However, routers can become neighbors if their hello intervals and hold times do not match.
The AS number is designed to control the routers with which a router can communicate. If the AS numbers do not match, EIGRP will not exchange routes between the two routers by design and definition.
The K-values are flags that state whether a certain metric component, such as Load, is used. They must match because they regulate how the metric values are calculated. If one router is just using bandwidth and delay to calculate its metric, and another is using bandwidth, delay, and load; they could make contradictory routing decisions that would lead to a routing loop. Because of this possibility, EIGRP requires that the K- values must match before it will allow the routers to exchange routes.
EIGRP does not require that the hello and hold times match. Although this flexibility can be helpful, it can also lead to unforeseen problems if they are accidentally mismatched. The hello interval is the amount of time in seconds to wait before sending another hello packet. The hold time is the amount of time in seconds to wait before declaring a link to be down.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify EIGRP neighbor relationship and authentication
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > Introduction to
EIGRP > How does EIGRP work?
QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit. The Los Angeles and New York routers are receiving routes from Chicago but not from each other
Which configuration fixes the issue?
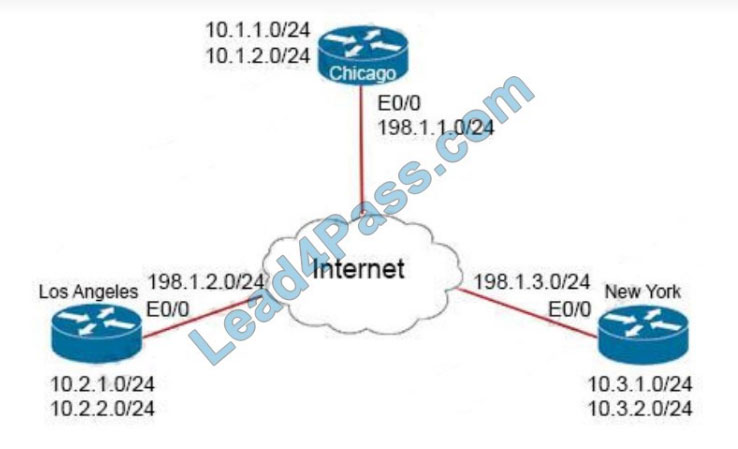

A. interface Tunnel1 no IP split-horizon eigrp 111
B. Interface Tunnel1 Ip next-hop-self elgrp 111
C. Interface Tunnel1 tunnel mode IPsec Ipv4
D. Interface Tunnel1 tunnel protection IPsec profile IPSec-PROFILE
Correct Answer: A
In this topology, the Chicago router (Hub) will receive advertisements from Los Angeles (Spoke1) router on its tunnel interface. The problem here is that it also has a connection with New York (Spoke2) on that same tunnel interface. If we don\’t disable the EIGRP split-horizon, then the Hub will not relay routes from Spoke1 to Spoke2 and the other way around.
That is because it received those routes on interface Tunnel1 and therefore it cannot advertise back out that same interface (split-horizon rule). Therefore we must disable split-horizon on the Hub router to make sure the Spokes know about each other.
QUESTION 5
When configuring Control Plane Policing on a router to protect it from malicious traffic, an engineer observes that the configured routing protocols start flapping on that device. Which action in the Control Plane Policy prevents this problem in a production environment while achieving the security objective?
A. Set the conform-action and exceed-action to transmit initially to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy in the output direction
B. Set the conform-action and exceed-action to transmit initially to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy in the input direction
C. Set the conform-action to transmit and exceed-action to drop to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy m the input direction
D. Set the conform-action to transmit and exceed-action to drop to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy m the output direction
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator configured redistribution on an ASBR to reach all WAN networks but failed Which action resolves the issue?
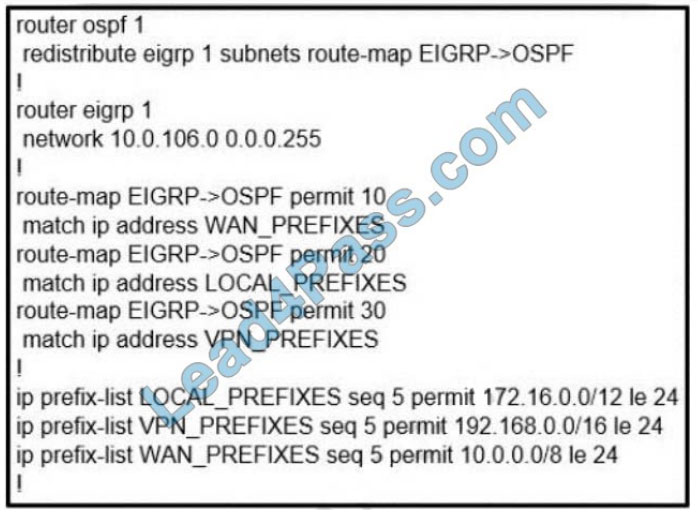
A. The route map must have the keyword prefix-list to evaluate the prefix-list entries
B. The OSPF process must have a metric when redistributing prefixes from EIGRP.
C. The route map EIGRP->OSPF must have the 10.0.106.0/24 entry to exist in one of the three prefix lists to pass
D. EIGRP must redistribute the 10.0.106.0/24 route instead of using the network statement
Correct Answer: A
In order to use a prefix-list in a route map, we must use the keyword “prefix-list” in the “match” statement.
For example:
match IP address prefix-list WAN_PREFIXES
Without this keyword, the router will try to find an access list with the same name instead.
QUESTION 7
Refer to the exhibit.
The server for the finance department is not reachable consistently on the 200.30.40.0/24 network and after every second month, it gets a new IP address. Which two actions must be taken to resolve this Issue? (Choose two.)
A. Configure the server to use DHCP on the network with default gateway 200 30.40.100.
B. Configure the server with a static IP address and default gateway.
C. Configure the router to exclude a server IP address.
D. Configure the server to use DHCP on the network with default gateway 200 30.30.100.
E. Configure the router to exclude a server IP address and default gateway.
Correct Answer: BC
QUESTION 8
Router10 is an area system border router (ASBR). The interfaces on Router 10 are configured as below: S 0/0 10.0.0.0/8 S0/1 172.16.0.0/8 Fa0/0 192.168.5.0/24 Fa0/1 192.168.6.0/24
You would like Router 10 to advertise the 192.168.5.0/24 and the 192.168.6.0/24 networks over OSPF in its Type 5 link-state advertisements (LSAs).
What command set would instruct the router to do this?
A. RTA10(config)# router ospf 1 RTA10(config-router)# redistribute static
B. RTA10(config)# router ospf 1 RTA10(config-router)# redistribute connected
C. RTA10(config)# router ospf 1 RTA10(config)# redistribute connected
D. RTA10(config)# router ospf 1 RTA10(config-router)# network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.0 area 1 RTA10(config-router)# network 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.0 area 1
Correct Answer: B
By default, Type 5 link-state advertisements (LSAs) do not include directly connected networks. To alter this behavior, you must execute the redistribute connected command in OSPF configuration mode. This command instructs the router
to
include these local interfaces in its advertisements, as follows:
RTA10(config)# router ospf 1
RTA10(config-router)# redistribute connected
You should not execute the command set that includes the redistribute static command. This instructs the router to
advertise any statically defined routes that have been configured, instead of those that are local to the router.
You should not execute the command set that includes RTA10(config)# redistribute connected. The redistribute
connected command is shown to be executed at the wrong command prompt and will generate an error message. It must be
executed in the OSPF configuration mode and not global configuration mode.
You should not execute the following command set:
RTA10(config)# router ospf 1
RTA10(config-router)# network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.0 area 1
RTA10(config-router)# network 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.0 area 1
The network commands will cause the networks to receive updates from the router but do not allow them to be
advertised in Type 5 LSAs.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify redistribution between any routing protocols or routing sources
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > Redistributing
Connected Networks to OSPF
QUESTION 9
Which statements about BGP policy-based routing are true? (Choose two.)
A. BGP policy-based routing is performed on a router\’s inbound interface.
B. A BGP administrator can use policy-based routing to alter the final destination of the packet.
C. BGP policy-based routing will select the next hop of the packet based on its source address.
D. BGP policy-based routing can be used to alter the path selection for a packet in a downstream AS.
Correct Answer: AC
BGP policy-based routing is performed on a router\’s inbound interface. BGP policy-based routing will select the next hop of the packet based on its source address. It does this through the use of route maps.
Below is a partial output of the show run command executed on a router that has a BGP configuration that uses a route map to alter the local preference of a route (172.16.0.0/16) to 90 if it is advertised from the BGP neighbor at 10.5.5.1:

The above output indicates that the local preference for the route to 172.16.0.0/16 is 90 ONLY if it comes from 10.5.5.1, but not if the same route is advertised from 10.5.5.35.
Route maps can be used to influence a part of the routing table without affecting the rest of the table. Consider an example where a router had two routes to every network in the table, and it prefers Neighbor A as the next hop for all routes. If you desired to change the next hop for one of the routes to Neighbor B without affecting the others, you could use route maps to take two different approaches, altering different attributes, which would arrive at the same result. The approaches would be:
Apply a route map to Neighbor B incoming that would set the local preference to 200 (default is 100) for the route. Local preference values determine the path used to exit the AS. A higher value is preferred. Apply a route map to Neighbor A
such that it advertises the route with a MED of 200. Med values determine the preferred path into the AS. A lower value is preferred. The default is 0.
Either of these approaches would result in the next hop for the network hanging to Neighbor B without affecting the others,
Policy-based routing does not alter the destination address of the packet. It can only alter the path to that final destination.
The BGP routing policy in one AS cannot determine the BGP routing policy in another AS.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Identify sub-optimal routing
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > Route-Maps for IP
Routing Protocol Redistribution Configuration
QUESTION 10
You have implemented OSPF for IPv6 for the following areas in OSPF AS 1:
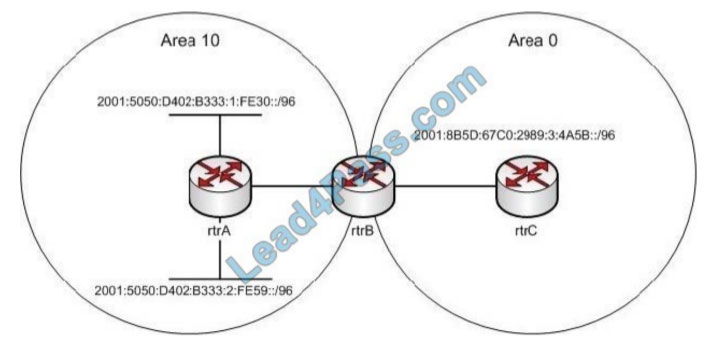
The cost from rtrB to the 2001:5050:D402:B333:1:FE30::/96 network is 80, while the cost from rtrB to the
2001:5050:D402:B333:2:FE59::/96 network is 130. Which of the following area range cost commands should be executed on rtrB?
A. area 10 range 2001:5050:D402:B333::/64 cost 80
B. area 10 range 2001:5050:D402:B333::/64 cost 130
C. area 10 range 2001:5050:D402:B333::/64 cost 210
D. area 10 range 2001:5050:D402:B333::/64 cost 0
Correct Answer: B
The area 10 range 2001:5050:D402:B333::/64 costs 130 commands that should be executed on rtrB. This command defines an area range for an area border router (ABR) that has OSPF for IPv6 enabled on it. This command provides a summary route of the routes in an OSPF area to be distributed to another area.
The range keyword in the command provides the summary route. The cost keyword in the command specifies the cost of the summary route. The highest cost of the routes that are being summarized becomes the cost of the summary route.
In this case, the cost from rtrB to the 2001:5050:D402:B333:1:FE30::/96 network is 80, and the cost from rtrB to the
2001:5050:D402:B333:2:FE59::/96 network is 130. The cost of the summary route is 130 as it is higher.
All the other options are incorrect because they do not specify the correct cost of the summary route.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify OSPF for IPv6
References: Cisco Learning Home > Groups > CCNP RandS Study Group > Discussions > What would be the Metric
for a Summary Route in OSPFv3 Cisco IOS IPv6 Configuration Guide, Release 12.4 > Implementing OSPF for IPv6 >
How to Implement OSPF for IPv6
QUESTION 11
Refer to the exhibit.
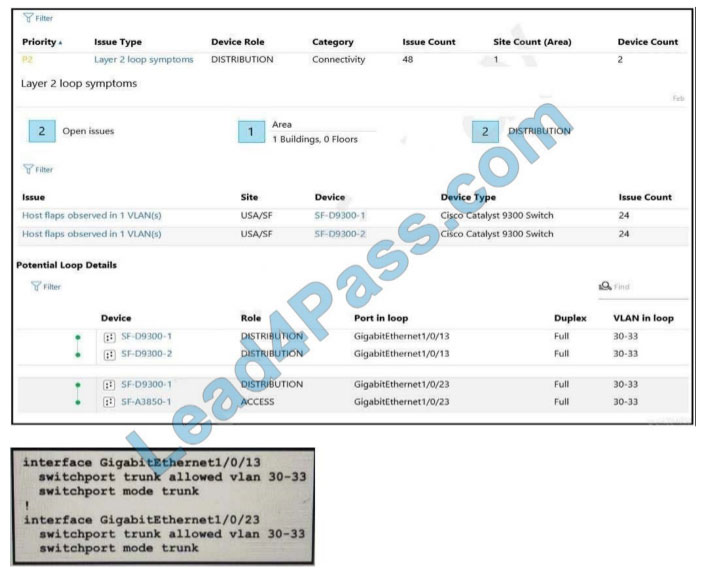
An engineer identifier a Layer 2 loop using DNAC. Which command fixes the problem in the SF-D9300-1 switch?
A. no spanning-tree uplink fast
B. spanning-tree loopguard default
C. spanning-tree backbone fast
D. spanning-tree portfast bpduguard
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION 12
An associate configured a serial connection on Router1 to use PPP with authentication. You execute the debug PPP negotiation command on the router and receive the following output:
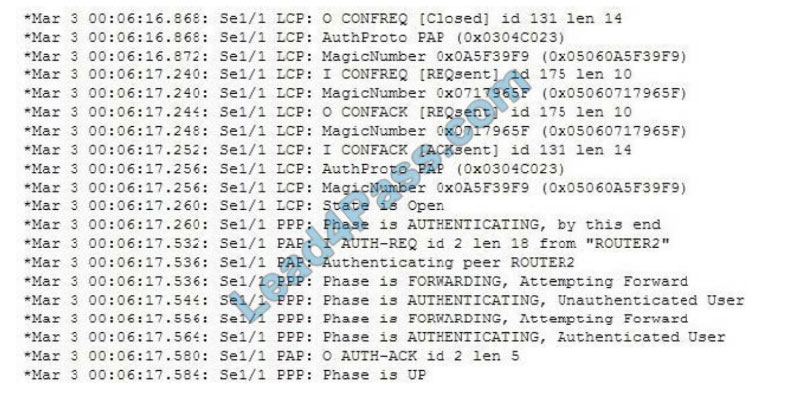
Which of the following statements are true? (Choose all that apply.)
A. the credentials are being sent in clear text
B. the connection failed
C. the peer\’s name is Router2
D. the authentication failed
Correct Answer: AC
The peer router\’s name is Router2 and the authentication method is PAP, which transmits the credentials in cleartext.
The peer name can be seen in the following line of output:
*Mar 3 00:06:17.536: Se1/1 PAP: Authenticating peer ROUTER2
The authentication protocol used is seen in the following line of output:
*Mar 3 00:06:16.868: Se1/1 LCP: AuthProto PAP (0x0304C023)
The connection process and authentication process are two separate processes and in this case, both succeeded. First,
the connection is completed as indicated by the following line of output:
*Mar 3 00:06:17.260: Se1/1 LCP: State is Open
Then later the authentication succeeded, as indicated by this line at the end of the output:
*Mar 3 00:06:17.584: Se1/1 PPP: Phase is UP
Objective:
Layer 2 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify PPP
References:
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Introduction > Troubleshoot and Alerts > Troubleshooting TechNotes > Configuring and Troubleshooting PPP Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
QUESTION 13
A CoPP policy is applied for receiving SSH traffic from the WAN interface on a Cisco ISR4321 router. However, the SSH response from the router is abnormal and stuck during the high link utilization. The problem is identified as SSH traffic does not match in the ACL. Which action resolves the issue?
A. Rate-limit SSH traffic to ensure dedicated bandwidth.
B. Apply CoPP on the control plane interface.
C. Increase the IP precedence value of SSH traffic to 6.
D. Apply CoPP on the WAN interface inbound direction.
Correct Answer: B
The problem is “SSH traffic does not match in the ACL” and “CoPP policy is applied for receiving SSH traffic from the WAN interface” so we should apply CoPP on the control plane interface instead.
……
300-410 Free dumps online download:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1FrKu52_Gnb_AA1sN0I7Js2SsCRQhMkma/view?usp=sharing
The leads4pass 300-410 dumps are really effective 300-410 ENARSI Exam prep material.
Use the 300-410 dumps https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html to ensure you pass the Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) exam with ease.

![[New May 2023] Updated 300-425 Dumps For 300-425 ENWLSD Exam](https://www.ciscoexampdf.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Updated-300-425-Dumps.jpg)
